Have you ever wondered why the heart, our vital pump, can sometimes falter in its duties? When we talk about symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure, we’re delving into a nuanced aspect of heart function that’s both fascinating and crucial to understand. But what exactly goes wrong when we say the “right side” of the heart is failing? Let’s explore this intriguing question together.
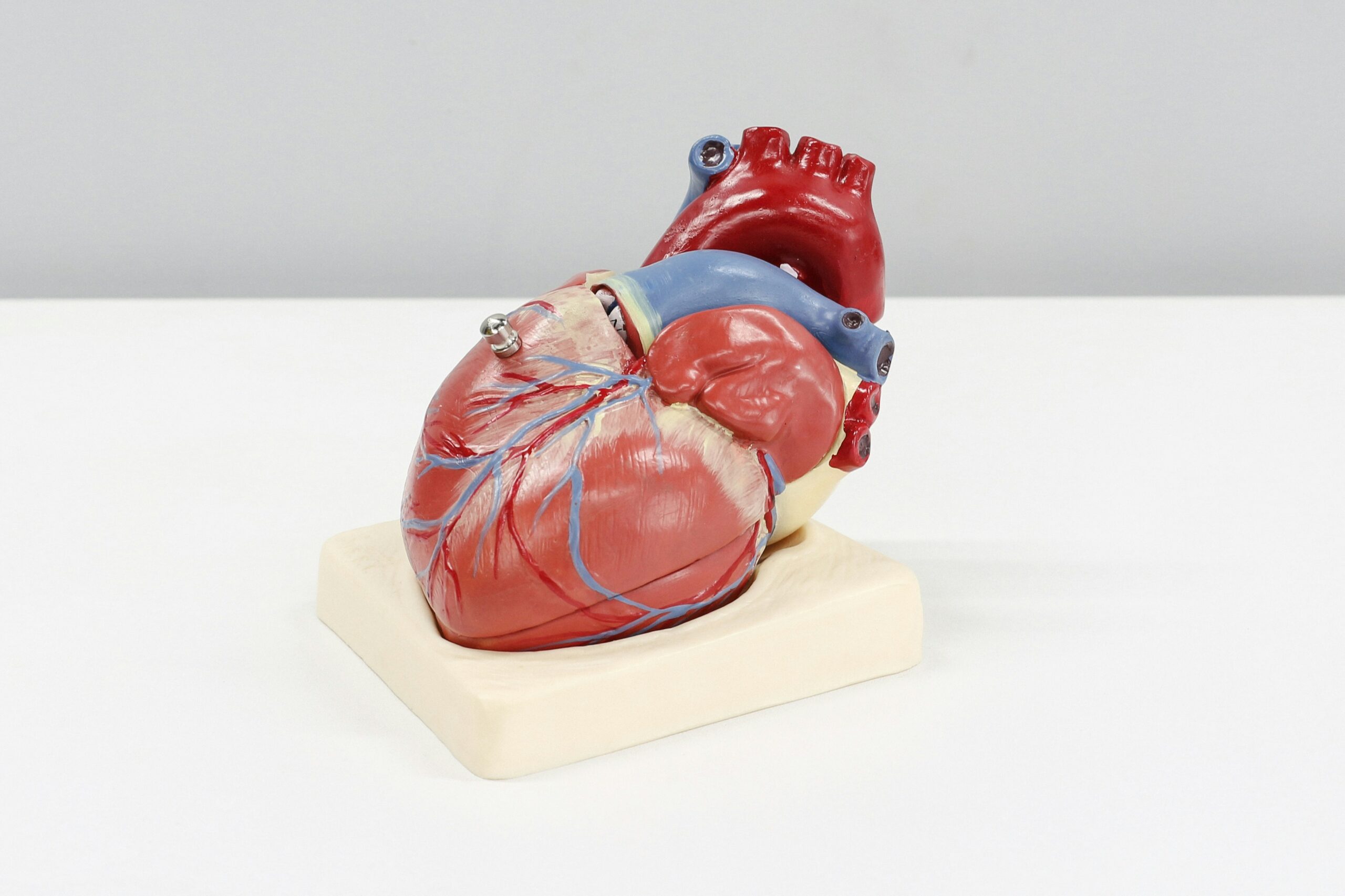
To grasp the essence of right sided heart failure, we must first understand the right ventricle’s role. Picture the heart as a bustling transport hub, with the right ventricle being the initial loading bay where blood begins its journey to the lungs. Here, blood is enriched with oxygen – a vital exchange that fuels every cellular process in our body. However, when this right ventricle faces challenges, it can lead to a cascade of issues, manifesting as symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure.
In a healthy heart, the right ventricle receives deoxygenated blood from the body’s veins and propels it towards the lungs with robust efficiency. But in right sided heart failure, the ventricle struggles to keep up. This could be due to the ventricle’s walls thickening, its chamber dilating, or it simply becoming too weak to contract effectively. The result? Blood begins to back up in the veins, leading to a series of symptoms that can include swelling in the legs and abdomen, as well as a sensation of fullness or discomfort.
It’s important to note that right sided heart failure often stems from left sided heart failure. When the left side of the heart can’t pump efficiently, it increases pressure in the pulmonary circulation, overloading the right side. This is a prime example of how interconnected our heart’s functions are, and why addressing symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure can be a complex task.
To visualize this, imagine a traffic jam on a major highway. If the main route (the left ventricle) is congested, the feeder roads (the right ventricle) inevitably suffer from the overflow. Similarly, when the left side of the heart is impaired, the right side faces increased pressure and workload, eventually succumbing to failure if not managed appropriately.
The pathophysiology of right sided heart failure is a testament to the heart’s delicate balance and interconnectedness. Understanding this balance not only helps us recognize the symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure but also underscores the importance of maintaining heart health through proactive measures.
In upcoming sections, we’ll delve into the risk factors that exacerbate this condition and explore how these insights can guide us in recognizing, diagnosing, and managing heart failure effectively. For now, let’s appreciate the marvel that is our heart and the critical role each of its components plays in our overall well-being.
Reference: Braunwald’s Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine, 11th Edition.
Have you ever paused to ponder why some individuals are more susceptible to heart issues than others? Understanding the risk factors for right sided congestive heart failure can be like solving a complex jigsaw puzzle, where each piece offers insights into prevention and management. Let’s dive into this puzzle and explore the factors that can tilt the scales towards heart failure on the right side.
When we talk about heart health, coronary artery disease (CAD) often takes center stage as a major player. This condition, characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, significantly affects the heart’s ability to function optimally. But how does it specifically impact the right side of the heart?
Coronary artery disease primarily affects the heart’s blood supply, leading to ischemia or reduced oxygen supply to the cardiac muscle. While this is typically associated with left sided heart failure, the right side isn’t immune. When the left ventricle is compromised due to CAD, it can lead to increased pressure in the pulmonary circulation. This, in turn, places additional stress on the right ventricle, making it a prime candidate for failure.
Imagine your heart as a complex water system, where the left side is the main pump and the right side ensures that the water reaches every corner of a garden. If the main pump falters due to blockages (akin to CAD), the entire system struggles, and the right side has to work harder to compensate, often leading to symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure.
But CAD isn’t the only factor at play. Other contributors include high blood pressure, which forces the heart to work against a higher resistance, and various lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which can increase the workload on the right side of the heart. Long-standing valvular heart diseases and congenital heart defects can also predispose individuals to right sided heart failure. American Heart Association – Right-Sided Heart Failure
Recognizing these risk factors is crucial for early intervention and management. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking cessation, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can mitigate these risks significantly. Moreover, regular check-ups become a vital tool, allowing healthcare providers to spot early signs of CAD and intervene before symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure manifest.
Understanding and addressing these risk factors is akin to maintaining your car’s engine; regular checks and maintenance can prevent breakdowns. As we move forward, let’s continue to piece together the heart’s complex puzzle, ensuring that each piece of information not only informs us but empowers us to take proactive steps towards heart health.
Reference: American Heart Association Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention.
Have you ever found yourself wondering if that persistent fatigue or swelling in your legs could be signaling something more serious? Recognizing the symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure is like tuning in to your body’s internal alarm system. These symptoms are vital signals that your heart needs attention. Let’s delve into these telltale signs and understand how they differ from those of left sided heart failure.
When it comes to heart failure, the symptoms can often be subtle and easily mistaken for less serious issues. However, differentiating between right and left sided heart failure symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Right sided heart failure primarily impacts the systemic venous system, leading to symptoms that reflect fluid accumulation in the body. One of the most common signs is peripheral edema, where fluid builds up in the tissues, causing swelling in the legs, ankles, and sometimes even the abdomen—a condition known as ascites. This symptom is a direct result of the right ventricle’s inability to efficiently pump blood, leading to a backlog in the venous system.
Another hallmark symptom is jugular venous distention, where the jugular vein in the neck appears swollen due to increased venous pressure. This is a visible sign that should prompt further investigation. Patients might also experience unexplained weight gain, frequent urination at night (nocturia), and a sense of bloating or fullness—symptoms that arise from fluid retention.
Contrastingly, left sided heart failure tends to present with symptoms related to pulmonary congestion. These include shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or while lying flat, and a persistent cough that may produce frothy sputum. The left ventricle’s failure to pump efficiently causes blood to back up into the lungs, leading to these respiratory symptoms.
The distinction between these symptoms is crucial. While both sides of the heart work in tandem, the manifestations of their failures are distinct, guiding healthcare providers in tailoring specific treatments. Recognizing the symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure not only aids in timely intervention but also helps in charting a course for effective management.
In our journey to understand heart health, recognizing these symptoms is akin to interpreting a complex language of the body. By tuning in to these signals, we can take proactive steps to address the underlying issues and support our heart’s health. As we continue exploring this topic, let’s remain vigilant in listening to what our body communicates, ensuring we respond with informed and timely actions.
Reference: Mayo Clinic’s Patient Care & Health Information on Heart Failure.
Have you ever felt like a detective, piecing together clues to solve a mystery? Diagnosing right sided congestive heart failure is much like solving a complex puzzle, where each test and examination provides a crucial piece of information. But how do healthcare professionals accurately diagnose this condition amidst a backdrop of overlapping symptoms? Let’s explore the diagnostic journey and the role of advanced imaging techniques in unveiling the truth.
When it comes to diagnosing right sided heart failure, imaging techniques play a pivotal role in providing a detailed picture of the heart’s structure and function. These tools are akin to having a magnifying glass in your detective kit, allowing for a closer examination of the heart’s intricacies.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is one such powerful tool. It offers detailed images of the heart’s anatomy and can assess the right ventricle’s size, function, and the presence of any structural abnormalities. MRI is particularly valuable in distinguishing between different types of heart failure and can help identify the specific cause, whether it be related to the heart muscle, valves, or congenital defects.
Computed Tomography (CT) scans are another essential diagnostic tool. They provide clear images of the heart and its surrounding structures, allowing doctors to evaluate the heart’s vessels and detect any blockages that might contribute to symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure. CT scans can also assess the lungs and other organs to rule out conditions that might mimic heart failure symptoms.
In addition to these imaging techniques, an echocardiogram is often used as a first-line diagnostic tool. It uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, providing information about the heart’s size, structure, and pumping efficiency. This test can help identify any underlying issues, such as valve disorders or pulmonary hypertension, that might cause or exacerbate right sided heart failure.
Together, these diagnostic tests allow healthcare providers to piece together the symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure with precision. They offer insights into the heart’s function and guide the development of a tailored treatment plan.
In the realm of heart health, these diagnostic tools are like the compass and map guiding us through uncharted territories. They help us navigate the complexities of heart failure, ensuring that each patient receives the most accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. As we continue our exploration of heart health, these technologies remind us of the power of innovation in transforming patient care.
For more information on treating congestive heart failure: read our article
Reference: American College of Cardiology’s Guidelines for Heart Failure Diagnosis.
Want to know how healthy your heart is?
Take our comprehensive test to identify potential risk factors and receive personalized recommendations for heart health.
Have you ever heard the phrase, “An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure”? When it comes to managing right sided congestive heart failure, lifestyle changes can be that ounce of prevention, offering a powerful defense against the progression of the disease. But what specific changes can make a tangible difference? Let’s uncover practical strategies that can help manage this condition and mitigate its symptoms.
Dietary choices are a cornerstone of managing right sided heart failure. The foods we consume have a profound impact on heart health, influencing factors like blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and fluid balance—all critical in managing heart failure symptoms.
Start with the basics: a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support heart health and reduce the risk of further cardiovascular complications. Think of your diet as the fuel that powers your body’s engine—choose high-quality fuel for optimal performance.
One crucial aspect of dietary management in right sided heart failure is sodium reduction. Excessive sodium intake can lead to fluid retention, exacerbating symptoms such as swelling in the legs and abdomen, which are common in right sided congestive heart failure. Aim to limit sodium intake by avoiding processed and packaged foods, and opt for fresh ingredients seasoned with herbs and spices instead.
In addition to sodium management, maintaining a healthy weight is vital. Excess weight can increase the heart’s workload, making it harder for the right ventricle to pump efficiently. Regular physical activity, tailored to your ability and condition, can help maintain weight and improve cardiovascular fitness.
Fluid management is another key consideration. In right sided heart failure, your doctor might recommend monitoring fluid intake to prevent overload. This involves tracking your daily fluid consumption, including all drinks and foods with high water content, to ensure you’re within the recommended limits.
Lastly, consider the role of lifestyle habits such as smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake. Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen levels in the blood, while excessive alcohol can weaken the heart muscle. Eliminating these habits can significantly enhance heart function and overall health.
Adopting these lifestyle changes is akin to tuning a finely crafted instrument—each adjustment contributes to harmony and balance. By taking proactive steps, you can manage the symptoms of right sided congestive heart failure and improve your quality of life. As we embrace these changes, let’s empower ourselves with the knowledge and actions that ensure our hearts continue to beat strong and steady.
Reference: American Heart Association’s Recommendations for a Heart-Healthy Diet.

© All Rights Reserved.