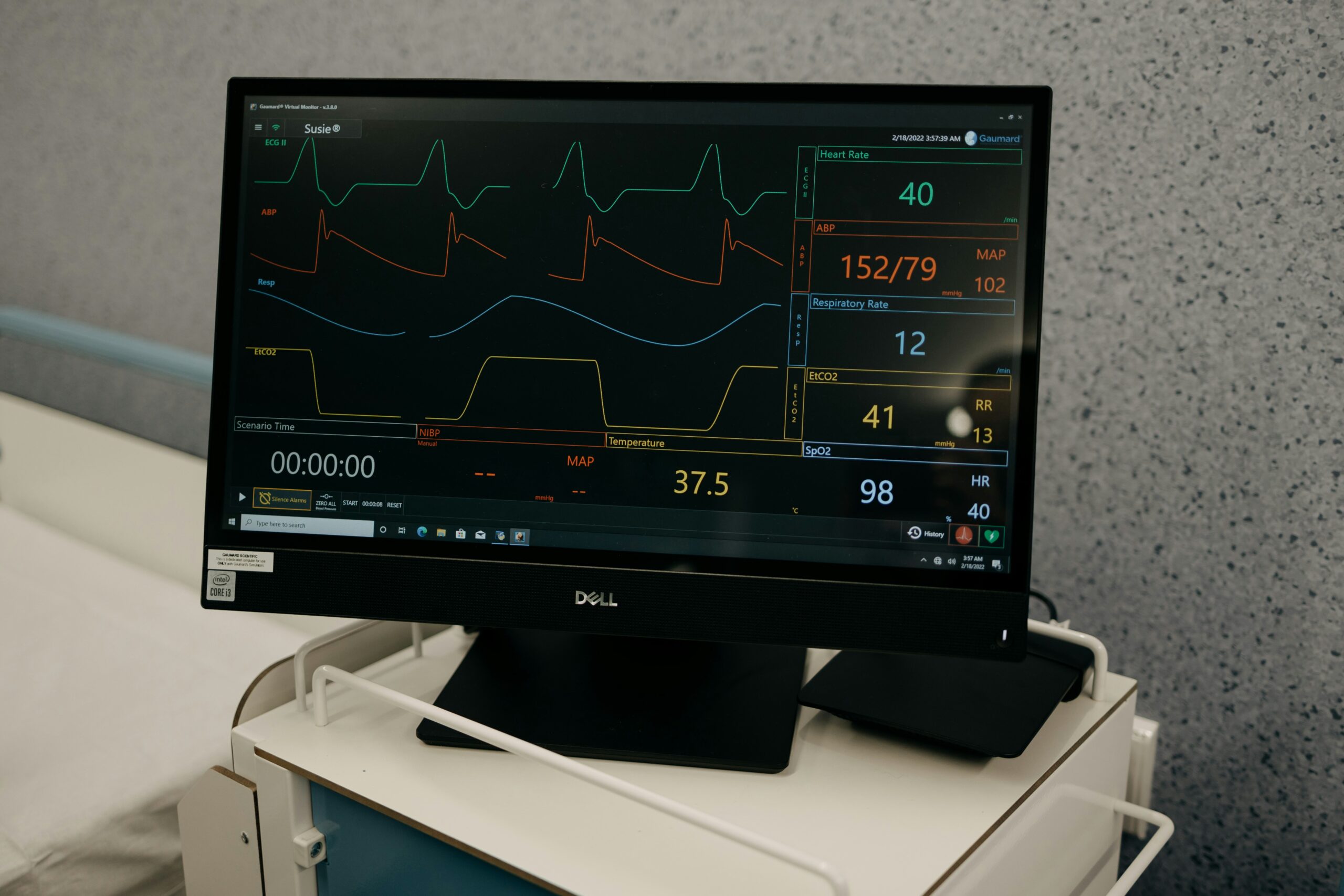
Top Foods to Boost Your Cholesterol Numbers: Incorporating Heart-Healthy Omega-3 Rich Foods
When it comes to managing high cholesterol, the question often arises: what is a good diet for high cholesterol? The answer, intriguingly enough, leads us straight to the ocean and the verdant fields. Let’s dive into the world of omega-3 rich foods—a key component of a diet designed to boost your cholesterol numbers positively.
Understanding Omega-3s and Their Role
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that our bodies can’t produce on their own. These fats are crucial for heart health and work wonders when it comes to managing cholesterol levels. But how exactly do they help? Omega-3s have been shown to reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, and even raise HDL (the “good” cholesterol) while reducing inflammation throughout the body. This combination of effects can significantly lower the risk of heart disease, making omega-3s a pivotal part of a good diet for high cholesterol.
The Seafood Connection
The most well-known sources of omega-3s are fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These fish are like the superheroes of the sea, packed with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)—two types of omega-3s that have been extensively studied for their heart health benefits. Aim to include these fish in your meals at least twice a week. Not a fan of fish? No worries, there are plant-based options too!
Plant-Based Omega-3 Sources
For those who prefer plant-based diets, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts are excellent sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3. While ALA isn’t as potent as EPA and DHA, your body can convert some of it into these more beneficial forms. Sprinkle chia seeds on your morning yogurt or blend them into smoothies. Flaxseed oil can be a great addition to salad dressings, providing a nutty flavor and a health boost.
Practical Steps to Omega-3 Rich Eating
Incorporating omega-3s into your diet doesn’t have to be a chore. Here are some practical steps:
- Fish Fridays (or any day!): Start a new tradition of enjoying a fish meal at least once a week. Grilled salmon with a side of vegetables is both delicious and heart-friendly.
- Snack Smart: Keep a bowl of walnuts handy for a quick snack. They’re more than just tasty—they’re doing wonders inside your body too.
- Breakfast Boost: Add a spoonful of chia seeds to your oats or smoothies. They’ll provide a satisfying crunch and a health kick.
By embracing these dietary changes, you’re not only addressing the need for a good diet for high cholesterol but also paving the way for a healthier, heart-friendly lifestyle. Keep in mind that consistency is key, so start small and gradually incorporate these heart-healthy habits into your everyday routine.
Learn more about tasty foods for heart health
Reference:
- American Heart Association. (2023). Omega-3 Fatty Acids. [https://www.heart.org]
Increasing Physical Activity for Better Cholesterol Levels: Cardiovascular Workouts and Their Effect on Cholesterol Levels
When we ponder what is a good diet for high cholesterol, it’s easy to focus solely on food. However, diet is just one piece of the puzzle. Physical activity, particularly cardiovascular workouts, plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels and promoting overall heart health. Let’s lace up our trainers and explore how moving your body can help boost your cholesterol numbers in the right direction.
The Dynamic Duo: Exercise and Cholesterol
Exercise and cholesterol management go hand in hand. Regular physical activity can help raise your levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as the “good” cholesterol, while simultaneously lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or the “bad” cholesterol. But how does this work? Exercise stimulates enzymes that help move LDL from the blood (and blood-vessel walls) to the liver, where it’s converted into bile and eventually excreted. Essentially, exercise helps clear the system of excess LDL, reducing the risk of plaque buildup in your arteries.
Cardiovascular Workouts to the Rescue
Cardiovascular workouts, often referred to as “cardio,” are activities that get your heart rate up and your blood pumping. These include walking, running, cycling, swimming, and even dancing. Engaging in these activities for at least 150 minutes a week can have a profound impact on your cholesterol levels. Not only do they help manage cholesterol, but they also contribute to weight loss, which is another important factor in heart health.
Making Cardio a Habit
Incorporating cardiovascular workouts into your routine doesn’t have to be daunting. Here are some tips to get started:
- Start Small: If you’re new to exercise, begin with short, manageable sessions. A brisk 10-minute walk around your neighborhood can be a great starting point.
- Mix It Up: Variety is the spice of life, and it applies to exercise too. Try different activities like cycling one day and swimming the next to keep things interesting.
- Set Realistic Goals: Aim for gradual progress. Whether it’s walking a bit longer or trying a new cardio class, small achievements can boost motivation.
- Buddy Up: Exercising with a friend or family member can make workouts more enjoyable and help keep you accountable.
The Synergy of Diet and Exercise
While exercise is a powerful tool for managing cholesterol, combining it with a good diet for high cholesterol can amplify the benefits. Consider your diet as the fuel that powers your exercise routine. Consuming heart-healthy foods like those rich in omega-3s, as we discussed earlier, provides the nutritional support your body needs to maximize the effects of your workouts.
In conclusion, cardiovascular workouts are a vital component of managing high cholesterol and maintaining overall heart health. By incorporating regular physical activity into your lifestyle, you’re not just addressing cholesterol concerns but also enhancing your quality of life. So, next time you consider what a good diet for high cholesterol entails, remember to include a healthy dose of movement as part of your plan.
Reference:
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023). Exercise and cholesterol: How much is enough? [https://www.mayoclinic.org]
Avoiding Trans Fats for Improved Cholesterol Health: Reading Food Labels and Identifying Hidden Trans Fats in Products
When exploring what is a good diet for high cholesterol, one critical element often sneaks under the radar—trans fats. These stealthy culprits play a significant role in raising your LDL cholesterol levels, thereby increasing the risk of heart disease. Let’s delve into the world of trans fats and discover how to spot them lurking within our food.
The Trans Fat Dilemma
Trans fats are a type of unhealthy fat that can wreak havoc on your cholesterol levels. They not only increase your LDL (bad cholesterol) but also lower your HDL (good cholesterol), creating a double whammy effect on your heart health. Originally created as a byproduct of hydrogenating vegetable oils to make them solid, trans fats are often found in processed and fried foods to enhance flavor and extend shelf life.
The Label Reading Challenge
Identifying trans fats in foods requires a keen eye and an understanding of food labels. While many countries have regulations requiring trans fat content to be listed on nutritional labels, they might still be present in products labeled as “0 grams of trans fat per serving.” This is because foods containing less than 0.5 grams per serving can be rounded down to zero.
Here’s how to outsmart these sneaky fats:
- Check the Ingredients: Look for terms like “partially hydrogenated oils” in the ingredients list. This indicates the presence of trans fats, even if the label claims otherwise.
- Be Wary of Processed Snacks: Many packaged snacks, baked goods, and margarine contain trans fats. Opt for fresh or minimally processed alternatives whenever possible.
- Examine Serving Sizes: Manufacturers might use small serving sizes to mask the trans fat content. Multiply the serving size to see how much you’re really consuming.
Practical Steps to Avoid Trans Fats
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and avoid trans fats hidden in restaurant and processed foods.
- Choose Healthy Alternatives: Opt for healthier fats like olive oil, avocado, and nuts instead of margarine or shortening.
- Read Labels: Make it a habit to read food labels and ingredient lists carefully. Awareness is your first line of defense against trans fats.
Combining Diet and Awareness
While understanding and avoiding trans fats is crucial, remember that this is just one component of a comprehensive approach to managing high cholesterol. A good diet for high cholesterol should focus on consuming heart-healthy foods and combining them with regular physical activity. This holistic approach will work in synergy to improve your cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
In summary, awareness and vigilance are your best tools in combating trans fats and their impact on cholesterol. By learning to read labels and make informed choices, you’re taking an essential step towards a heart-healthy lifestyle. So, next time you reach for a snack or a pre-packaged meal, take a moment to consider the trans fat content—your heart will thank you.
Reference:
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. (2023). Trans Fats. [https://www.hsph.harvard.edu]
Exploring Different Types of Cholesterol: Understanding the Role of LDL and HDL Cholesterol in the Body
When considering what is a good diet for high cholesterol, it’s crucial to understand the types of cholesterol that play significant roles in our body’s health. Let’s unravel the mystery of LDL and HDL cholesterol, their distinct functions, and how they influence your heart health.
The Duality of Cholesterol: LDL vs. HDL
Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in your blood, is essential for building healthy cells. However, not all cholesterol is created equal. It comes in two primary forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Understanding their roles is key to managing high cholesterol effectively.
- LDL Cholesterol: The “Bad” Cholesterol
LDL cholesterol is often labeled the “bad” cholesterol because high levels can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, narrowing them and potentially leading to blockages. Think of LDL as a delivery truck, dropping off cholesterol to various parts of your body. When there’s too much of it, these trucks start piling up, creating traffic jams in your arteries. - HDL Cholesterol: The “Good” Cholesterol
HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, is considered the “good” cholesterol. Its role is to act like a cleanup crew, picking up excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transporting it back to the liver for disposal. Higher levels of HDL are associated with a lower risk of heart disease because they help clear away the cholesterol that could otherwise clog your arteries.
Influencing Cholesterol Levels with Diet
A good diet for high cholesterol aims to lower LDL and raise HDL levels. Here’s how you can influence these levels through dietary choices:
- Increase Soluble Fiber: Foods like oats, beans, and lentils are rich in soluble fiber, which helps reduce LDL levels by binding to cholesterol particles and removing them from the body.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Replace saturated fats found in red meats and butter with healthier fats from olive oil, nuts, and avocados to help improve your cholesterol balance.
- Embrace Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, can help boost HDL levels and provide additional heart-protective benefits.
Beyond Diet: Lifestyle Factors
While diet plays a significant role, lifestyle factors such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking significantly impact your cholesterol levels. Engaging in physical activity, as discussed earlier, can raise your HDL levels, providing a dual benefit when combined with dietary changes.
Understanding the interplay between LDL and HDL cholesterol is crucial when determining what is a good diet for high cholesterol. By making informed dietary and lifestyle choices, you can positively influence these cholesterol levels and support your heart health. Remember, it’s about finding a balance that works for you, ensuring both your LDL levels are kept in check and your HDL levels are optimized.
Reference:
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023). Cholesterol Levels: What You Need to Know. [https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov]
Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet: Differentiating Between Healthy and Unhealthy Fats for Heart Health
When we delve into what is a good diet for high cholesterol, the role of dietary fats often becomes a topic of confusion. Not all fats are harmful, and in fact, some are essential for maintaining optimal cholesterol levels and overall heart health. Let’s navigate the world of fats and understand how to incorporate the beneficial ones into your diet.
The Great Fat Divide: Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats
Fats can be broadly categorized into healthy and unhealthy types, each affecting your cholesterol levels differently. Understanding this distinction is crucial in making heart-healthy dietary choices.
- Unhealthy Fats: The Culprits
Unhealthy fats primarily include saturated and trans fats. Saturated fats, found in animal products like red meat and full-fat dairy, can raise LDL cholesterol levels. As we discussed earlier, trans fats are even worse, increasing LDL while lowering HDL cholesterol, thus posing a significant risk to heart health. - Healthy Fats: The Heart Helpers
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, have the opposite effect. They can lower LDL cholesterol and are beneficial for heart health. These fats are found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fish.
Incorporating Healthy Fats into Your Diet
The key to a good diet for high cholesterol is embracing healthy fats while minimizing unhealthy ones. Here’s how you can make the transition:
- Choose Plant-Based Oils: Swap butter and lard for healthier oils like olive, canola, or avocado oil. These oils are rich in monounsaturated fats that help lower bad cholesterol levels.
- Go Nuts: Nuts and seeds, particularly almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds, are excellent sources of healthy fats and make for a great snack or salad topper.
- Embrace Fatty Fish: Incorporate fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines into your meals. They’re rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health by lowering triglycerides and inflammation.
- Avocado Love: Avocados are not just delicious but also packed with heart-healthy fats. Use them as a spread, in salads, or even as a base for creamy dressings.
Bringing It All Together
While understanding the types of fats is vital, the broader context of your diet and lifestyle should not be overlooked. Complement these dietary changes with regular physical activity and other heart-healthy habits for a comprehensive approach to managing high cholesterol.
In conclusion, embracing healthy fats is an integral part of what constitutes a good diet for high cholesterol. By consciously choosing foods rich in beneficial fats and avoiding those high in unhealthy ones, you can make a significant impact on your cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Remember, it’s not about eliminating fats but choosing the right ones for a heart-friendly diet.
Reference:
- American Heart Association. (2023). Dietary Fats: Know Which Types to Choose. [https://www.heart.org]