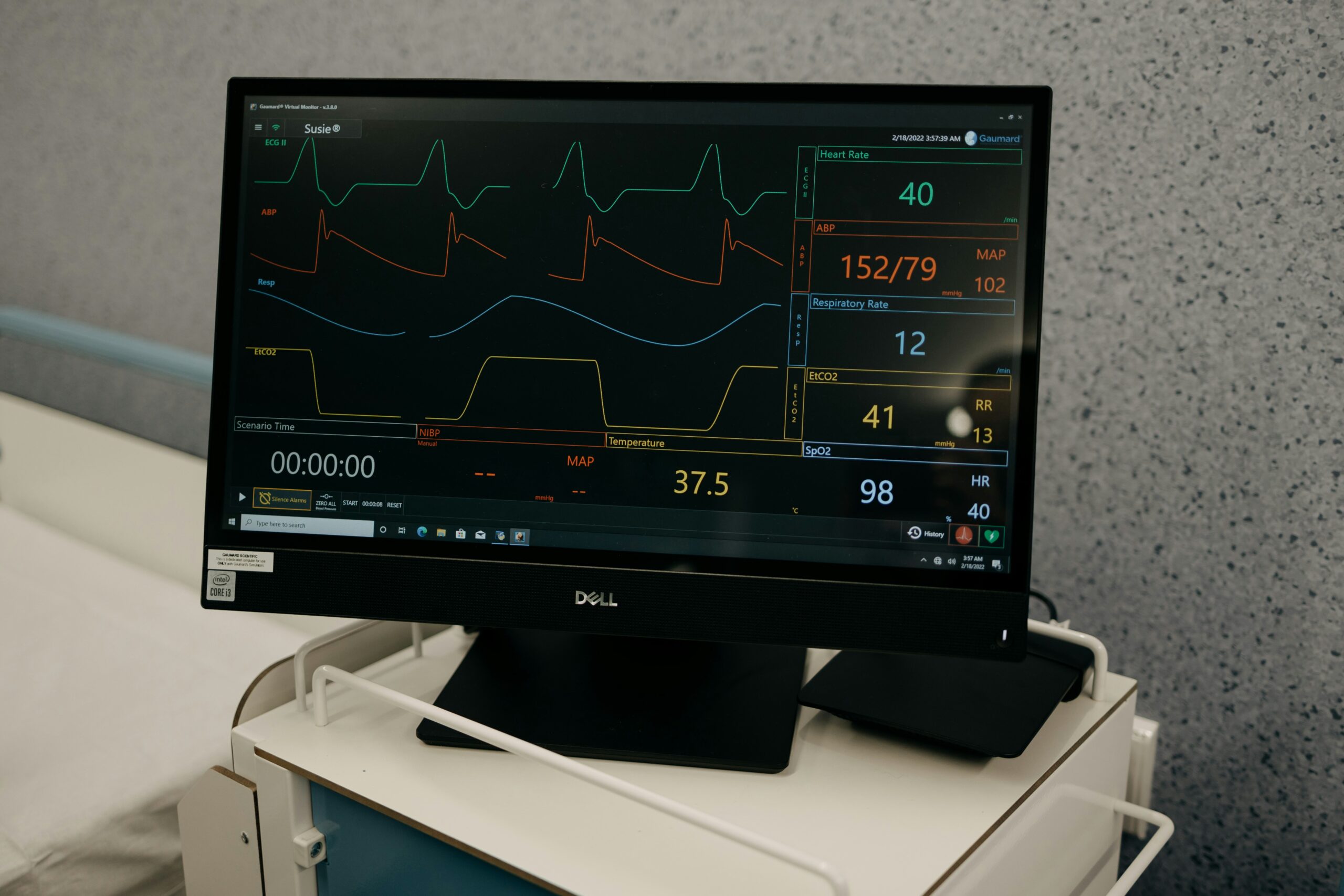
Detecting Atrial Fibrillation Early: Why Timely Diagnosis is Crucial
Importance of Symptom Recognition: Identifying Early Signs of Atrial Fibrillation
Imagine sitting in your favorite coffee shop, sipping a warm cup, when suddenly your heart starts racing out of the blue. It’s disconcerting, isn’t it? These unexpected heart palpitations, along with fatigue or shortness of breath, might be more than just a fleeting moment of anxiety. They could be early signs of atrial fibrillation, or AFib as we often call it. Recognizing these symptoms early on is like catching a whisper before it becomes a shout.
Atrial fibrillation can sometimes feel like that erratic punk band you heard once—chaotic and unpredictable. Many of us might dismiss these episodes as stress or just “one of those days,” but ignoring these signs can lead to more serious heart problems down the road. The tricky part is that AFib doesn’t always throw a party with obvious symptoms. Sometimes, it’s silent, making regular check-ups crucial for detecting those elusive rhythms and maintaining cardiovascular health.
When we think about our heart, it’s not just a muscle, but our very life force. It’s important we listen to it. If anything feels off, such as an irregular heartbeat or unexpected pulse changes, don’t just chalk it up to a bad day. Seek guidance, because an early diagnosis can be a real game-changer. For more on AFib symptoms and risks, refer to the American Heart Association’s AFib Guide.
Treatment Outcomes: How Early Detection Improves Management of Atrial Fibrillation
Catching AFib early is like spotting a storm on the horizon while there’s still time to take shelter. Early detection is pivotal because it opens the door to a host of management options that can significantly improve outcomes. Picture this: when we identify AFib in its early stages, we can better tailor treatments to prevent complications like stroke—a risk that looms large with untreated AFib.
When diagnosed early, treatment strategies can be more effective and less invasive. We can employ lifestyle modifications, medications, or even procedures like cardioversion to restore a normal heartbeat. It’s akin to tuning an instrument before it gets too far out of tune.
Moreover, early diagnosis allows for closer monitoring and timely intervention. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of stroke but also enhances quality of life. We can maintain the harmony of our heart’s electrical signals, rather than constantly playing catch-up.
It’s a bit like having a roadmap before embarking on a journey; knowing the path helps us navigate with confidence, avoiding risk factors along the way. So, let us be vigilant, listen to our heart’s cues, and seek timely medical advice. After all, it’s our heart’s heartbeat that sets the rhythm of our lives.
Reference: January, C. T., Wann, L. S., Alpert, J. S., Calkins, H., Cigarroa, J. E., Cleveland, J. C., … & Yancy, C. W. (2014). 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. *Journal of the American College of Cardiology*, 64(21), 2246-2280.
Anticoagulation Therapy: Understanding Who Needs It and When
Role of Anticoagulants: Preventing Blood Clots in Atrial Fibrillation Patients
Imagine the heart as a grand conductor, orchestrating the music of life through every heartbeat. But what happens when the rhythm goes awry, as it might with atrial fibrillation? It’s like an orchestra losing its tempo, and in such chaos, blood clots can form, posing a significant risk of stroke. This is where anticoagulants, often referred to as blood thinners, step into the spotlight, ensuring that the music continues without a hitch.
Anticoagulants work by reducing the blood’s ability to clot, which is crucial for patients with AFib, as they are at a higher risk of stroke. It’s a bit like adding a safety net under a tightrope walker; it doesn’t prevent falls entirely, but it drastically reduces the risk of severe injury if a fall occurs. The decision to start anticoagulation therapy, however, isn’t taken lightly.
Doctors often use a tool called the CHA2DS2-VASc score, which assesses stroke risk in AFib patients based on various factors like age, heart failure, hypertension, and diabetes. If you’re wondering why such a detailed assessment is necessary, it’s because anticoagulation therapy comes with its own set of risks, primarily bleeding. Thus, the benefits must outweigh these risks.
Deciding who needs anticoagulation therapy and when to start it is about finding that delicate balance. It’s a collaborative decision between you and your healthcare provider, ensuring that you’re protected without unnecessary risks.
In this journey of managing AFib, anticoagulants are like the unsung heroes, playing a crucial role in safeguarding against stroke. They allow us to embrace a future where we can enjoy life’s symphony without missing a heartbeat.
Reference: Hart, R. G., Pearce, L. A., & Aguilar, M. I. (2007). Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. *Annals of Internal Medicine*, 146(12), 857-867.
Types of Cardiac Monitoring for Atrial Fibrillation: Exploring Options
Implantable Loop Recorders: Long-Term Monitoring for Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosis
Consider this: atrial fibrillation can be a bit like a ghost—sometimes there, sometimes not, and often elusive when you try to catch it. That’s where implantable loop recorders (ILRs) come in, serving as our dedicated ghost hunters in the world of cardiology.
ILRs are small, under-the-skin devices that monitor your heart’s electrical signals over long periods. Imagine having a vigilant sentinel, always on the lookout for those sneaky, irregular heartbeats that can signify AFib. They’re particularly useful for patients who experience infrequent symptoms, making it difficult to catch AFib in the act during a standard ECG or Holter monitor test.
The beauty of an ILR is its capability for long-term monitoring—up to three years! It’s like having a personal cardiologist in your pocket, recording and analyzing your heart rhythms day and night. This can be a game-changer for diagnosing AFib, especially when episodes are sporadic and unpredictable.
Of course, the decision to opt for an ILR is not made in isolation. It’s a collaborative discussion with your healthcare provider, weighing benefits such as the comprehensive data it provides against factors like invasiveness and cost.
In the grand scheme of cardiovascular health, ILRs offer a window into the world of your heart’s rhythm, catching those ghostly arrhythmias that might otherwise go unnoticed. With this continuous monitoring, we can tailor treatments more effectively, ensuring that our hearts remain in sync and free from the shadows of AFib.
Reference: Hindricks, G., Pokushalov, E., Urban, L., Taborsky, M., Kuck, K. H., Lebedev, D., … & Pürerfellner, H. (2010). Performance of a new implantable cardiac monitor in detecting and quantifying atrial fibrillation. *Heart Rhythm*, 7(7), 969-977.
Preventing Atrial Fib and Stroke: Effective Strategies for Heart Health
Smoking Cessation: How Quitting Smoking Can Reduce the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke
Smoking—the friend that harms in disguise. It may feel comforting in stressful times, but in reality, it’s one of the major risk factors for atrial fibrillation and stroke. Each puff is like a small chisel, slowly wearing down the integrity of your heart and blood vessels. Learn more about how nicotine affects the body and erodes health from within: Read the article
Quitting smoking is perhaps one of the most impactful lifestyle changes we can make for our heart health. When we stop smoking, we don’t just reduce the risk of AFib; we also significantly lower the chances of a stroke. It’s like putting down that chisel and allowing the heart to heal and strengthen.
The connection between smoking and AFib is rooted in the way smoking affects our cardiovascular system. It increases blood pressure, reduces oxygen in the blood, and promotes inflammation—all of which are detrimental to heart health. These changes create a fertile ground for atrial fibrillation, akin to setting the stage for an unwanted performance.
But here’s the silver lining: the benefits of quitting smoking begin almost immediately. Within just 20 minutes, heartbeat and blood pressure drop. Over time, the risk of heart diseases plummets, offering us a chance to rewrite our heart’s story with a happier, healthier ending. To learn more about quitting smoking, explore American Cancer Society’s Guide to Quitting Smoking.
Of course, quitting smoking is no small feat. It’s a journey, often requiring support, whether through counseling, medication, or support groups. But remember, every step taken is a step towards a heart that’s robust and free from the shadows of AFib and stroke. It’s about reclaiming control and allowing our heart to sing its true, unencumbered melody.
Reference: Huxley, R. R., & Woodward, M. (2011). Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for coronary heart disease in women compared with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. The Lancet, 378(9799)